
Introduction to Biomedical
Informatics and Artificial Intelligence
AMIA-OHSU 10x10 Program
Logistics, Curriculum,
Learning Objectives, and Additional Information

 |
|
Introduction to Biomedical
Informatics and Artificial Intelligence
|
|
 |
| Unit |
Topic |
| 1 |
Overview of Fields and
Motivating Problems |
| 2 |
Computing Concepts for Biomedical Informatics |
| 3 |
Electronic and Personal Health Records (EHR, PHR) |
| 4 |
Standards and Interoperability |
| 5 |
Artificial Intelligence |
| 6 |
Advanced Use of the EHR |
| 7 |
EHR Implementation, Security, and Evaluation |
| 8 |
Information Retrieval (Search) |
| 9 |
Research Informatics |
| 10 |
Other Areas of Informatics |
| Unit |
Topic |
Textbook Chapter(s) |
| 1 |
Overview of Fields and Motivating Problems | 1, 2 |
| 2 |
Computing Concepts for Biomedical Informatics | 3, 23 |
| 3 |
Electronic and Personal Health Records (EHR, PHR) |
4, 7 |
| 4 |
Standards and Interoperability | 5 |
| 5 |
Artificial Intelligence | 6, 8, 21 |
| 6 |
Advanced Use of the EHR | 9, 10 |
| 7 |
EHR Implementation, Security and Evaluation | 11, 12, 13, 22 |
| 8 |
Information Retrieval (Search) |
14 |
| 9 |
Research Informatics |
15, 16 |
| 10 |
Other Areas of Informatics |
17, 18, 19, 20 |
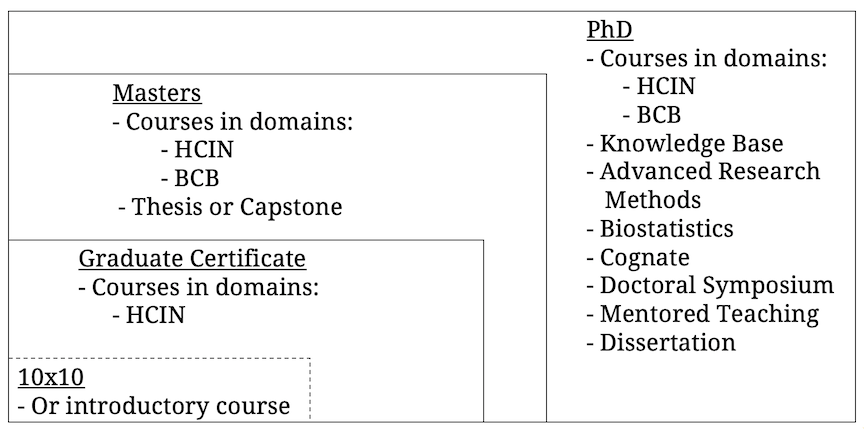
| Program
Name |
Description |
Graduation Requirements |
| Graduate Certificate |
Core courses in informatics |
21 credits (7 3-credit
courses) |
| Master of Science Non-Thesis |
"Professional" master's
degree with capstone or internship project |
49 credits (43 hours of
instruction plus 6 hours of capstone/internship project) |
| Master of Science |
"Research" master's degree
with master's thesis |
55 credits (43 hours of instruction plus 12 hours of master's thesis) |
| Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) |
PhD program for advanced
leaders and researchers in field |
135 credits, including
dissertation |